GitLab 9.5, the last 9.x release before GitLab 10.0, is available with improvements to navigation, new project templates with pre-configured CI, and new automation features for CI and performance.
The new navigation streamlines UI and reduces the number of clicks it takes to move through a GitLab instance. It also comes with newly added icons and subnav on hover. In 9.5, GitLab introduces Project Templates, allowing developers to quickly create new projects that have pre-configured CI. It’s also possible to automatically retry failed jobs ran with GitLab CI/CD.
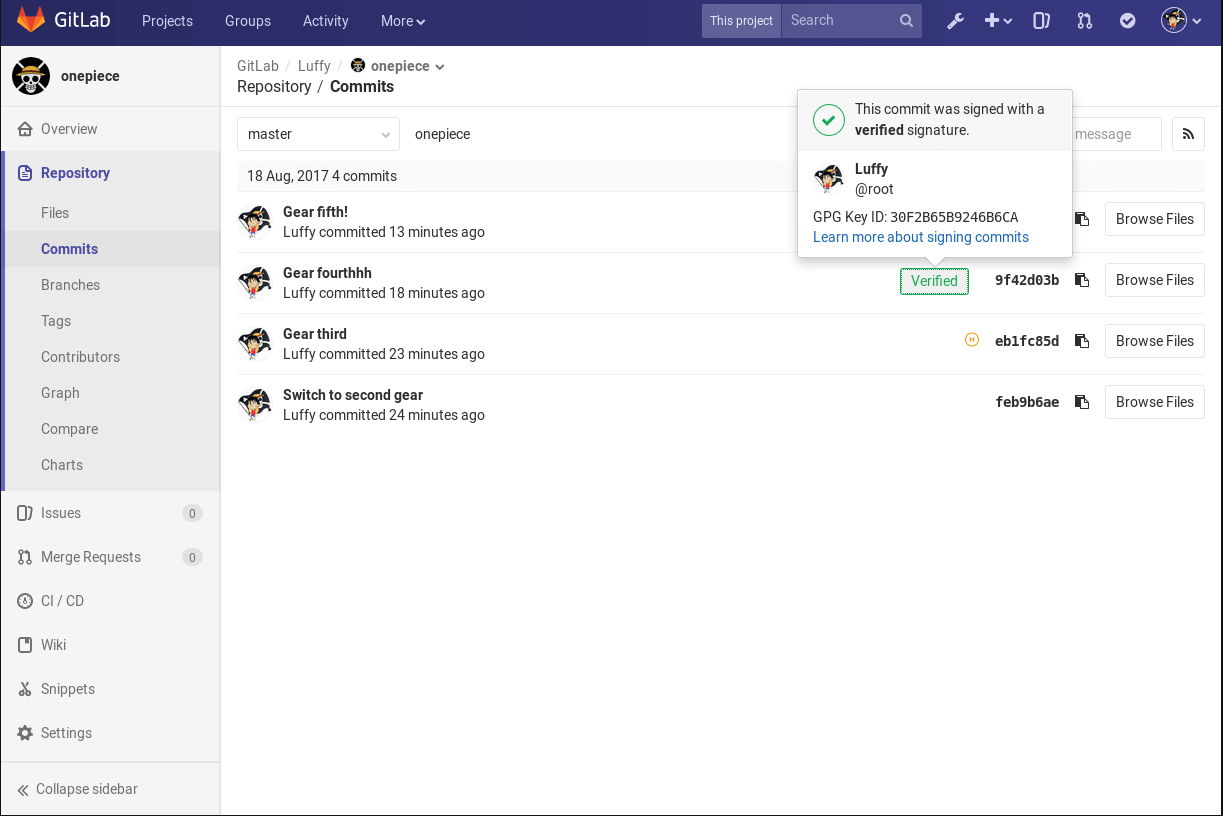
The other big update to GitLab is the GPG Commit Verification feature. According to a blog post:
“When you commit a change in Git, you tell Git who the author is. This is not verified, meaning a bad actor could create a commit that looks like it was made by the original author. GPG signed commits solves this problem by allowing you to sign your commits, proving that you’re the original author (because only you have the private key that matches the public key).”
There are additional improvements to the development lifecycle, and GitLab 9.5 also comes with the addition of Automatic Monitoring for Auto Deployed applications.
Xcode 9: New refactoring engine
Xcode 9 includes a brand new refactoring engine, which aims to transform code locally within a single Swift source file. According to a Swift blog post, the logic behind local refactorings is implemented entirely in the compiler and SourceKit, and it’s now open source in the swift repository.
Any Swift developer can contribute refactoring actions to the open source language. In the blog post it reviews how a simple refactoring can be implemented and surfaced in Xcode. For instance, a local refactoring occurs within the confines of a single file. Examples of this refactoring includes Extract Method and Extract Repeated Expression. More information can be found here.
IEEE standard for quantum computing
IEEE and the IEEE Standards Association announced the approval of the IEEE P7130 – Standard for Quantum Computing Definitions project, which aims to make quantum computing more accessible to contributors like developers, material scientists, engineers, and more.
“While Quantum Computing is poised for significant growth and advancement, the emergent industry is currently fragmented and lacks a common communications framework,” said William Hurley, chair, IEEE Quantum Computing Working Group. “IEEE P7130 marks an important milestone in the development of Quantum Computing by building consensus on a nomenclature that will bring the benefits of standardization, reduce confusion, and foster a more broadly accepted understanding for all stakeholders involved in advancing technology and solutions in the space.”
The project defines terms related to the physics of quantum computing, including quantum tunneling, super position, and quantum entanglement. Related terms and terminology will be updated as technological advances are made, according to the IEEE.
Google Chrome Enterprise
In order to give companies a single and cost-effective solution, Google announced Chrome Enterprise, a host of features like access to enterprise app storefronts, security controls, support, and integration with cloud and on-premise management tools.
The new Chrome Enterprise license will also offer Google Play, managed OS updates, theft prevention, application virtualization support, cloud and native print, and more. Chrome Enterprise gives customers the ability to manage all their Chrome devices from a single management solution, which means IT admins across the organization can work with their broad range of devices.
More information is available here.






