The latest edition of the OWASP Top 10 showed that all of the highest-priority vulnerabilities since 2017 have shifted and new ones have been introduced.
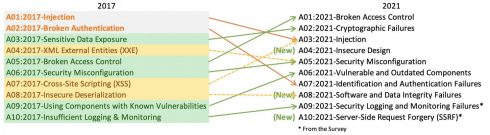
Broken Access Control has dethroned Injection as the top vulnerability, whereas it previously held fifth place. The 34 Common Weakness Enumerations (CWEs) mapped to Broken Access Control had more occurrences in applications than any other category, according to the OWASP Top 10 2021.
Cryptographic Failures (which was previously known as Sensitive Data Exposure) moved up from third to second place. The renewed focus here is on failures related to cryptography which often leads to sensitive data exposure or system compromise.
Injection slid down to third, with Cross-site Scripting now qualifying as part of this category.
New categories of vulnerabilities this year included Insecure Design, Software and Data Integrity Failures, and Server-Side Request Forgery.
This latest edition of the OWASP Top 10 is more data-driven than before with eight of the ten categories from contributed data and two categories from an industry survey at a high level.
“Previous data collection efforts were focused on a prescribed subset of approximately 30 CWEs with a field asking for additional findings. We learned that organizations would primarily focus on just those 30 CWEs and rarely add additional CWEs that they saw,” the OWASP creators wrote on the list’s website that contains additional details.
This iteration opened up the categories and just asked for data with no restrictions on CWEs. It asked for the number of applications tested for a given year starting in 2017, and the number of applications with at least one instance of a CWE found in testing.
“This format allows us to track how prevalent each CWE is within the population of applications,” the OWASP creators added.
The vulnerabilities were ranked as:
- Broken Access Control
- Cryptographic Failures
- Injection
- Insecure Design
- Security Misconfiguration
- Vulnerable and Outdated Components
- Identification and Authentication Failures
- Software and Data Integrity Failures
- Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
- Server-Side Request Forgery