GitHub wants to improve security with new capabilities and best practices for account security and recoverability.
The company announced it will be enforcing more secure passwords by creating its own version of the project HaveIBeenPwned.com, which users could use to check for passwords that were found in available sets of breach data. The dataset is made up of 517 million records available, which is how GitHub is replicating the service internally.
Effective today, users with compromised passwords will be asked to change their password during login, registration, or when updating their password. The company recommends signing up for HaveIBeenPwned notifications as well.
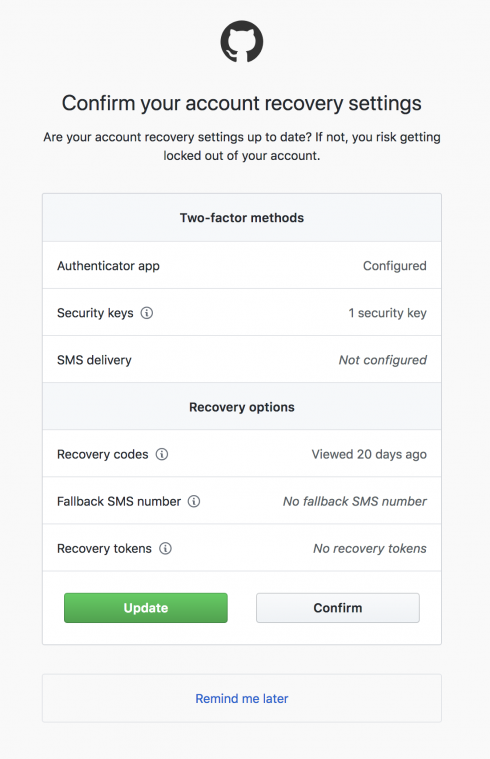
In accordance with the best practice of using two-factor authentication, GitHub will now prompt users to periodically review their two-factor authentication setup and recovery options. Losing access to your two-factor credentials can result in you losing access to your account, so by requiring users to keep their credentials up-to-date, this risk can be minimized, the company explained.
GitHub suggest that having a hardware U2F key is a secure option for two-factor authentication. It also recommends storing two-factor backup codes in a password manager or secure physical location, as well as linking your GitHub account to Facebook via Recover Accounts Elsewhere.
In addition, GitHub recommends reviewing other GitHub credentials such as SSH keys, deploy keys, OAuth authorizations, and personal access tokens. The company does remove those that have not been used in a year, but still recommends reviewing them periodically.