Microsoft Research is working on a new programming language designed around cloud-first development and artificial intelligence. As part of its work, the company announced new capabilities for the Bosque programming language created to support automated reasoning tools.
According to Microsoft, Bosque derives from a combination of TypeScript inspired syntax and types plus ML and Node/JavaScript inspired semantics.
The language was created to simultaneously support a high productivity development experience that modern cloud developers expect, while also providing a resource efficient and predictable runtime with a performance profile similar to a native C++ application.
“The move into cloud based development, with architectures based around microservices, serverless functions, and RESTful APIs, brings new challenges for development. In this environment an program may interoperate with many other (remote) services which are maintained by different teams (and maybe implemented in different languages),” Microsoft wrote in a blog post. “The Bosque project takes a cloud and IoT first view of programming languages. Thus, it includes features like API Types to simplify the construction and deployment of REST style APIs.”
The combination of choices such as fully determinized language semantics, keys and ordering, and memory behavior result in a runtime with minimal performance variability and to enable ultra-low overhead tracing, according to Microsoft.
The main features of the language include immutable values, block scoping – which is very appealing for structuring code according to Microsoft -, named arguments along with rest and spread operators that can be used to perform simple and powerful data manipulation as part of invocations and constructor operations.
“Bosque is about connecting a constrained core-language IRs to a developer friendly and high-productivity programming experiences,” said Mark Marron, a principal research software development engineer (SDE) at Microsoft Research in the webinar Expanding the possibilities of programming languages with Bosque.
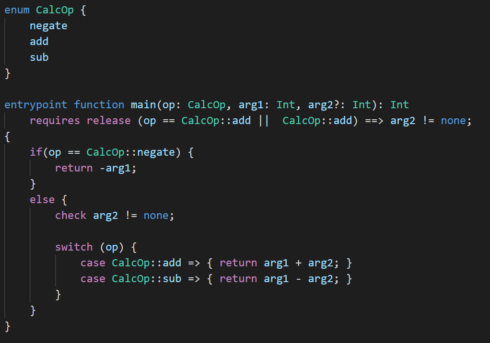
The Bosque language also includes reference parameter threading via ‘ref’ argument passing, an alternative to multi-return values that simplifies scenarios where a variable is passed to a method. In addition, it provides two flavors of typed strings, ‘SafeString<T>’ and ‘StringOf<T>,’ to address various scenarios where including meta-data about the string in the type is useful.
“If you’re going to upgrade a dependency, you can check if it is possible that this new dependency is going to change the behavior of your application somewhere and allow you to do version upgrades much more quickly and confidently,” Marron said.
Marron added that one limitation that Bosque currently has is that there is currently no IO support or runtime, but Microsoft Research is working with Morgan Stanley to integrate Bosque and use their runtime.
Additional details about the Bosque programming language are available here.