The Angular team is detailing new tools and practices developers can take in order to decrease their initial load times and speed up page navigation. The team goes over code splitting, preloading strategies, performance budgets and efficient serving to help developers gain and retain their users.
When it comes to initial load time, the team recommends minification and dead code elimination and code-splitting. In version 8 of Angular, the CLI was updated with differential loading support, which separates bundles for modern or legacy JavaScript browsers.
RELATED CONTENT: Angular 8 released with builder APIs and web worker support
“One of the most expensive types of assets in an app is JavaScript. Once the browser downloads a JavaScript file, it often has to decompress it, after that parse it, and finally execute it. That is why it’s critical for the performance of an app to ship fewer bytes of JavaScript during the initial load time,” Minko Gechev, Angular engineer, wrote in a post.
Code-splitting enables developers to control how to decrease JavaScript bundles, according to Gechev. The approaches to code-splitting include component level code-splitting and route level code-splitting. Component level code-splitting allows users to “load individual components lazily even without a route navigation” while route level code-splitting enables users to “load the individual routes lazily. For example, if the user is in the home page of an app and they navigate to the settings page, Angular will first download the corresponding bundle and after that render the route,” Gechev wrote.
Developers can use ngx-loadable and @herodevs/hero-loader libraries to help code-splitting on a component level.
For route-level code-splitting, Angular added a new command that enables users to generate a lazy module in a single command instead of having to write boilerplate code.
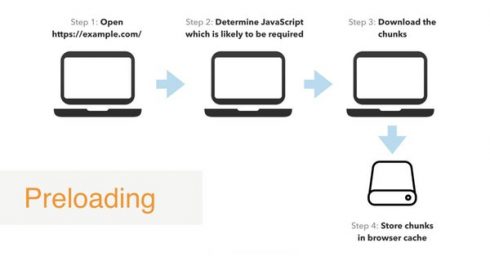
The Angular team also added a preloading strategy for routes to ensure good UX. “Once we introduce a lazy route in our app, when the user navigates to it, Angular will first download the corresponding bundle from the network. On a slow internet connection, this could lead to a bad UX,” Gechev explained.
Angular provides quicklink for preloading modules associated with visible links and predictive prefetching for preloading modules that will likely be needed next.
In order to ensure performance won’t regress over time, the team also introduced performance budgets. “To monitor our apps over time, the Angular CLI supports performance budgets. The budgets allow us to specify limits in which the production bundles of our app can grow,” Gechev wrote.
Lastly, the team introduced a new deploy command for producing efficient builds and deploying apps to a selected hosting provider.
More information is available here.






