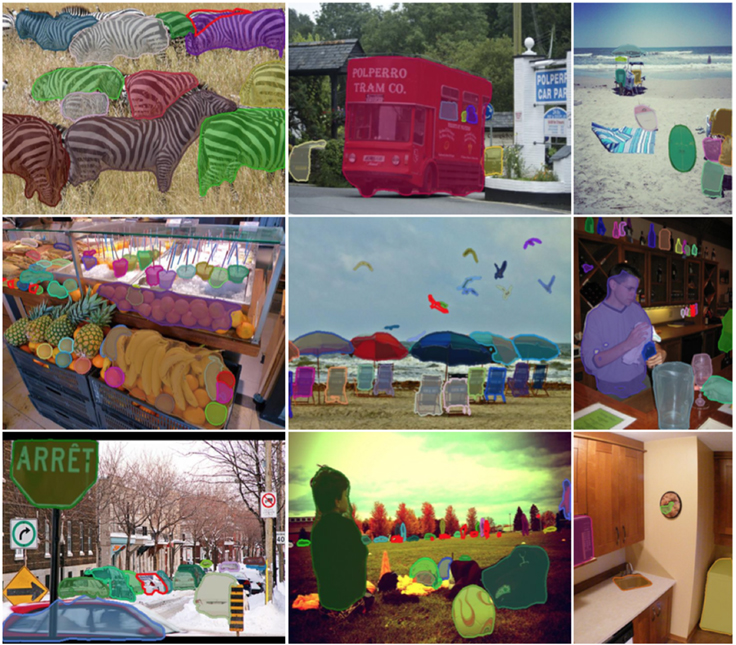
Humans can easily identify objects down to the very last pixel, and Facebook AI Research (FAIR) wants to push its machine vision capabilities and get machines to understand images and objects at the pixel level too. To do so, FAIR has introduced new algorithms and frameworks this week.
Recently, FAIR has been designing new techniques that identify and segment objects as images, and this capability will enable new applications, the company said. The algorithm driving these advances is the DeepMask segmentation framework, which works with the new SharpMask segment refinement module. Together these frameworks enable FAIR’s machine vision systems to detect and identify every object in images.
FAIR’s MultiPathNet is a specialized convolutional net, which can label each object mask with the object type it contains. The code for DeepMask, SharpMask and MultiPathNet will be accessible to developers, and FAIR hopes they will help advance the field of machine vision, according to a FAIR blog post.
Navisens announces seed funding and new technology
Software-based location platform Navisens is introducing a new indoor and outdoor tracking technology that doesn’t rely on GPS, WiFi or Bluetooth. According to the company, the location solution is designed to leverage motion sensors in smartphones, making it more reliable than alternative location solutions.
“GPS has become ubiquitous, and that’s actually a big problem for developers trying to create apps that work in urban environments or need a more refined reading of movement,” said Ashod Donikian, CEO and founder of Navisens. “GPS wasn’t created for use in urban environments, no matter how much it’s assisted by cell towers and WiFi access points or Bluetooth beacons. But every smartphone comes with motion sensors, which our software reads in a unique way so that it can tell where your phone is located indoors, outdoors and underground, along with the direction it’s facing and whether the device is stationary or in use.”
Navisens’ motionDNA is available as a native iOS or Android SDK.
In addition, the company is announcing a US$2.6 million round of seed funding led by Resolute Ventures.
Rackspace wants to go private
The managed cloud platform Rackspace announced it has entered into a definitive agreement with affiliates of Apollo Global Management to be acquired for US$32 per share. The total transition is valued at $4.3 billion, and would make Rackspace a privately held company.
“We are also excited that this transaction will provide Rackspace with more flexibility to manage the business for long-term growth and enhance our product offerings,” said Graham Weston, cofounder and chairman of the board of Rackspace. “We are confident that as a private company, Rackspace will be best positioned to capitalize on our early leadership of the fast-growing managed cloud services industry.”
The transition is expected to close during the fourth quarter of this year.
Preventing MIME confusion attacks in Firefox
Starting with Firefox 50, Firefox will MIME confusion attacks, an exploit that uses with MIME sniffing, according to Mozilla.
“Firefox will reject stylesheets, images or scripts if their MIME type does not match the context in which the file is loaded if the server sends the response header ‘X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff,’ ” wrote Christoph Kerschbaumer, security and privacy engineer at Mozilla.
Also, if the Content-Type of a file doesn’t match the context, Firefox will block the file and prevent a MIME confusion attack, according to Kerschbaumer. It will then display a message in the console, he wrote.