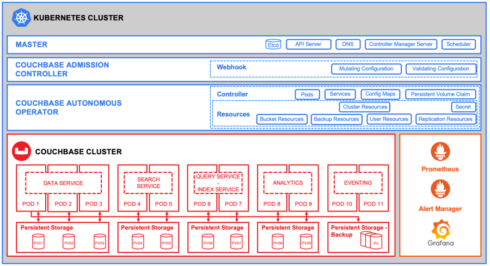
Couchbase Autonomous Operator for Kubernetes 2.0 introduces enterprise-grade capabilities including security, resource management, monitoring, high-availability, and cross-cloud compatibility.
This enables self-service access to the database while standardizing development, test, pre-production, and production environment. It also reduces operational complexity up to 95% by implementing the operational best practices that most efficiently deploy and manage Couchbase, according to the company in a post.
“The Autonomous Operator enables Couchbase Server to be run next to microservices applications on the same Kubernetes platform. This eliminates infrastructure silos caused by having to run stateful database applications separately to the container-based microservices they support,” Couchbase wrote.
Stackery achieves AWS Lambda Ready Designation
The announcement differentiates Stackery’s secure serverless delivery platform as fully integrated with AWS Lambda.
Stackery helps enterprise teams design, develop, and deliver modern applications on AWS quickly, securely, and at scale.
Earlier this month, the company expanded its capabilities for DevOps teams, including GitOps workflows that facilitate changes, audits, and delivery mechanisms and integrations with CircleCI, Jenkins, Gitlab, and more.
Additional details are available here.
DigitalOcean announces Virtual Private Cloud and the new Trust Platform
DigitalOcean VPC enables users to run resources such as Droplets VMs, Kubernetes clusters, Managed Databases, and Load Balancers within a private network.
VPC allows users to create multiple private networks for their account or their team, instead of having just one private network and allow them to configure Droplets to behave as Internet gateways.
Meanwhile, the Trust Platform is a website that provides users one place to get all of their security and privacy questions answered, and to download available security certifications.
Additional details are available here.
V8 introduces wasm-decompile
V8 introduced wasm-decompile due to the growing number of compilers and other tools that generate or manipulate .wasm files.
Wasm-decompile produces output that tries to look like a “very average programming language” while still staying close to the Wasm it represents.
Additional details on how it works are available here.