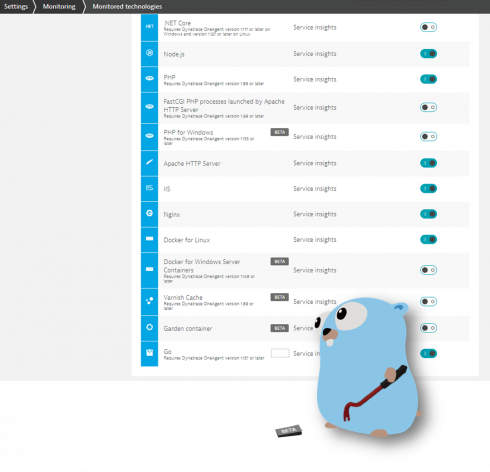
Dynatrace is now offering automatic code level insights on applications that use Go. Dynatrace will automatically discover and monitor Go components so that developers do not need to inject code into microservices or change the code of Go applications.
Dynatrace believes this capability will help organizations that use high profile cloud platforms that were built with Go. It enables DevOps teams to focus on optimizing applications rather than troubleshooting them.
“Go is lightweight, suited to microservices architectures and fast becoming the most utilized programming language of the cloud. Yet most monitoring tools are blind to Go which has left organizations having to do manual development and configuration to get any sort of insight,” said Steve Tack, SVP of product management at Dynatrace. “The Dynatrace platform is built for the cloud and now automatically detects and shines a light into Go components, ensuring that Go isn’t creating an enterprise cloud blind spot.”
Java Card 3.1 is now available
Oracle has announced that Java Card 3.1 is now available. Java Card is a platform used for securing sensitive devices.
The update provides users with more flexibility in meeting hardware and security requirements of existing chips and new IoT technologies.
New emerging applications of Java Card include wearables, automotive, cloud-connected devices, and smart meters and industrial IoT.
Mozilla closes its Test Pilot Program
Mozilla has announced that after three successful years, it is closing its Test Pilot Program and moving to a new structure for innovation. The new structure will involve even more user input and testing.
Mozilla has stated that many Test Pilot experiments will move to Addons.Mozilla.Org, while others, such as Send and Lockbox will continue to be worked on, innovated, and eventually evolved into stand alone products.
Google Cloud Functions now supports Go 1.11
Google Cloud has announced that Cloud Functions now supports Go 1.11, which is the latest version of Go. Go 1.11 includes new features, such as modules for integrating third-party dependencies into code.
“Using Cloud Functions, you can build serverless application backends, real-time data processing pipelines, chatbots, and video or image analysis tools, just to name a few. Now, you can also use the familiar building blocks of Go to build out your Cloud Functions,” Google Cloud wrote in a post.